Intersection
The functions intersections and selfIntersections find intersections between a pair of triangle meshes, or between a mesh and itself.
Intersections are meaningful only for meshes that have an extrinsic geometry, encoded via an EmbeddedGeometryInterface (e.g. a VertexPositionGeometry). These routines assume the meshes are triangle meshes, but otherwise works with arbitrary polygon soup (encoded via SurfaceMesh).
Intersections are returned as an “edge soup,” i.e., a collection of line segments with no explicit connectivity between shared endpoints.
Triangle-triangle intersections are computed using Tomas Moller’s 1997 triangle intersection routine, provided here.
all-pairs check
The current implementation does a naive all-pairs check, which takes O(nm) time (or O(n^2) time in the case of self-intersections). This makes the methods very slow for large meshes. A natural future improvement would be to perform hierarchical collision checking.
#include "geometrycentral/surface/intersection.h"
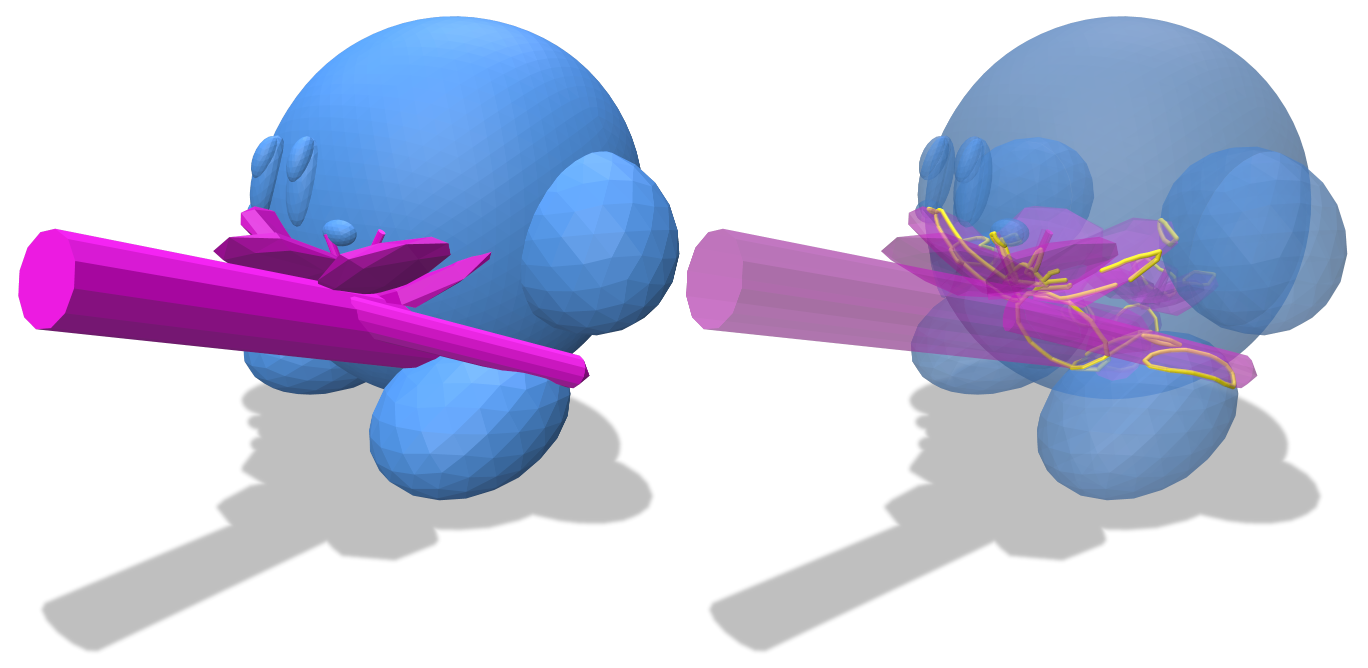
SurfaceIntersectionResult intersections(EmbeddedGeometryInterface& geometry1, EmbeddedGeometryInterface& geometry2);
Find all intersections between two meshes.
geometry1: the geometry of the first meshgeometry2: the geometry of the second mesh
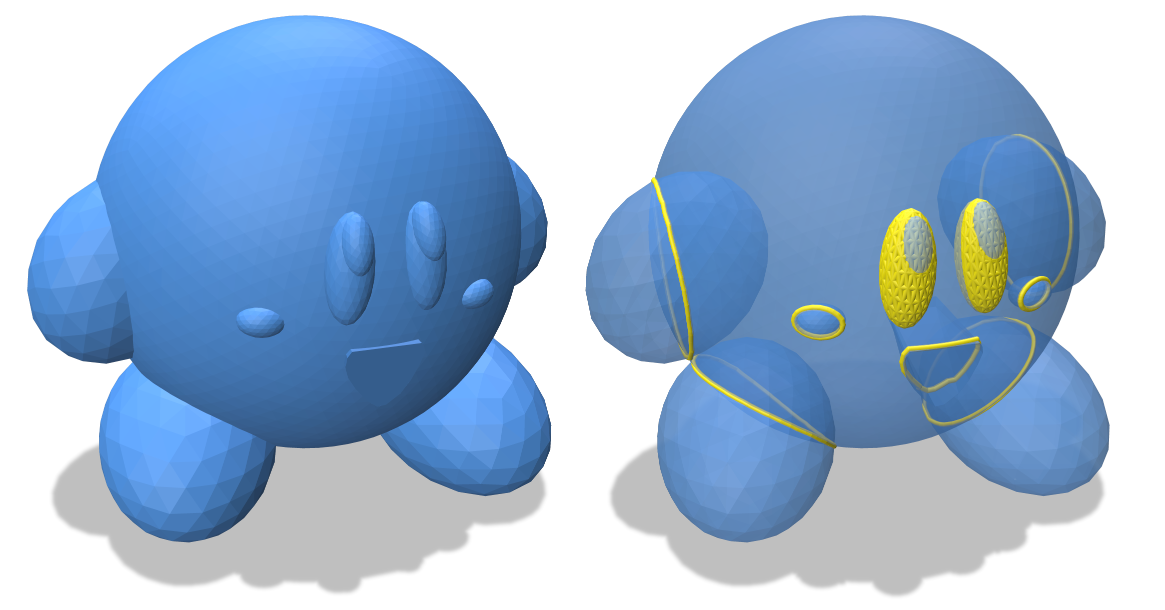
SurfaceIntersectionResult selfIntersections(EmbeddedGeometryInterface& geometry);
Find all intersections between non-adjacent pairs of triangles in a single mesh, i.e., triangles that do not share vertices or edges. (Adjacent triangles are excluded, since otherwise we would find all the mesh vertices and edges in addition to more global intersections.) Note that for polygon soup, where triangles have identical vertex locations but there is no explicit connectivity, intersections will still be found between adjacent triangles (such as the triangles in the eyes of the model pictured above).
geometry: the input geometry
Example
#include "geometrycentral/surface/surface_mesh.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/meshio.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/intersection.h"
// Load two meshes
std::unique_ptr<SurfaceMesh> mesh1, mesh2;
std::unique_ptr<VertexPositionGeometry> geometry1, geometry2;
std::tie(mesh1, geometry1) = readSurfaceMesh(filename1);
std::tie(mesh2, geometry2) = readSurfaceMesh(filename2);
// Find self-intersections in mesh1
SurfaceIntersectionResult r1 = selfIntersections( *geometry1 );
// Find intersections between the two meshes
SurfaceIntersectionResult r12 = intersections( *geometry1, *geometry2 );
Helper Types
Result
The result is returned as a SurfaceIntersectionResult, which has 3 fields:
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
SurfacePoint endPoint |
the point the path ended at |
std::vector<Vector3> points |
endpoints of segments along intersection |
std::vector<std::array<size_t,2>> edges |
segments along intersection, as pairs of indices into the points list |
bool hasIntersections |
were there any intersections? |