Surface Sampling
Poisson disk sampling
The PoissonDiskSampler class contains a function that Poisson disk-samples a surface mesh so that each pair of sampled points are at a minimum distance r away from each other. This ensures that sampled points are distributed evenly in 3D space. Technically, Poisson disk sampling on surfaces should ensure that points are at least a certain geodesic distance away from each other. But for the purposes of visualization, it can be better to use extrinsic distance of the embedded surface instead, since this will ensure that the sampling looks even – two points could have a large geodesic distance between them but be very near each other in 3D space, which might lead to a visually crowded image.
Currently the algorithm only works on manifold meshes.
#include "geometrycentral/surface/poisson_disk_sampler.h"
The algorithm has a few parameters that roughly correspond to the algorithm of Bridson’s 2007 Fast Poisson Disk Sampling in Arbitrary Dimensions.
Additionally, you can specify points around samples should be avoided (shown in red below.)
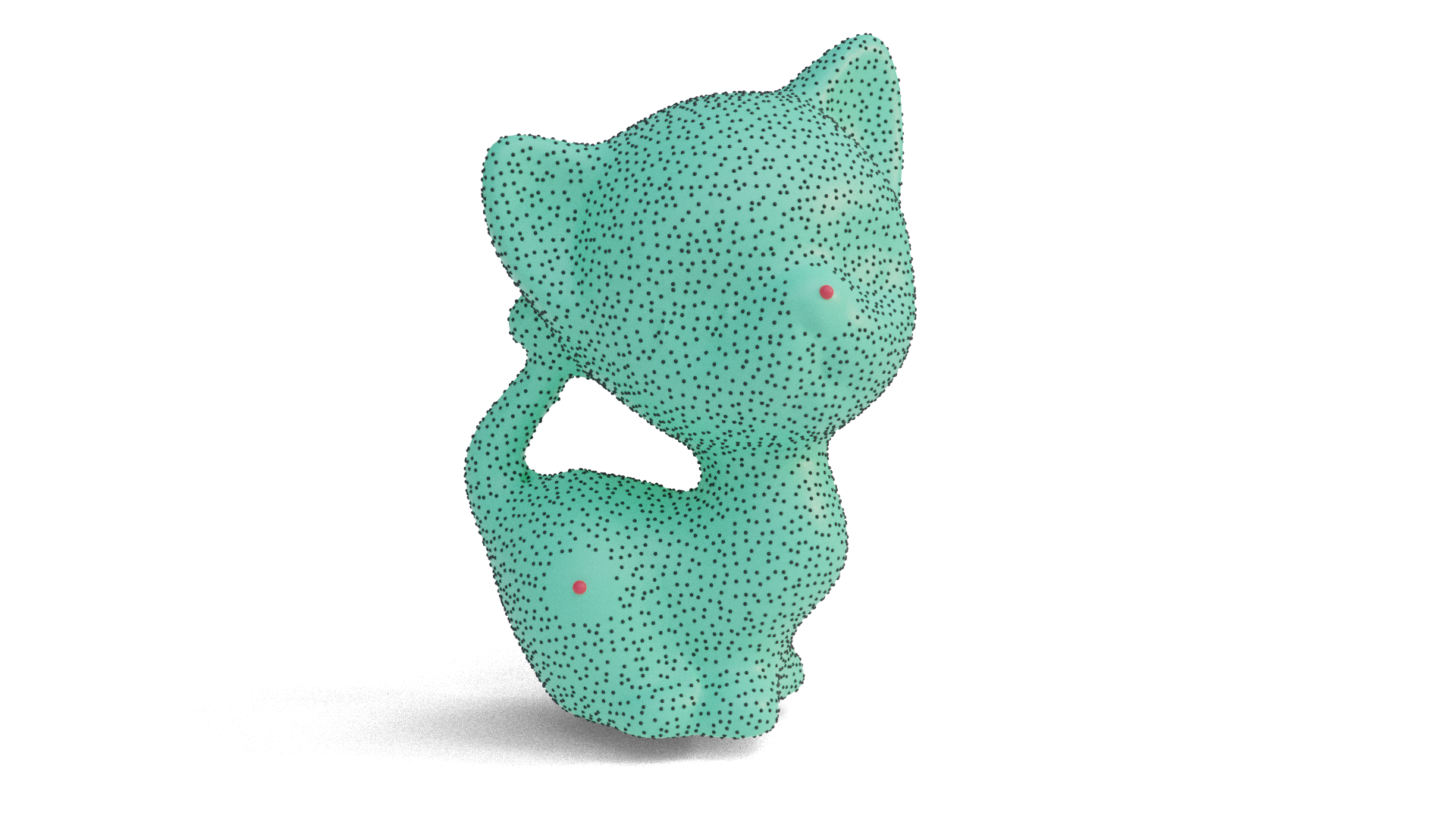
PoissonDiskSampler::PoissonDiskSampler(ManifoldSurfaceMesh& mesh, VertexPositionGeometry& geometry)
Create a new solver to Poisson disk-sample on the given mesh with the given geometry.
meshspecifies the mesh. It must be manifold, since the sampling depends on thetraceGeodesicfunction.geometryspecifies theVertexPositionGeometryneeded to describe the positions of vertices in 3D space.
The mesh and geometry cannot be changed after construction.
std::vector<SurfacePoint> sample(const PoissonDiskOptions& options = PoissonDiskOptions())
Poisson disk-sample the surface mesh.
Example
#include "geometrycentral/surface/manifold_surface_mesh.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/vertex_position_geometry.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/meshio.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/surface_point.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/poisson_disk_sampler.h"
// Load a mesh
std::unique_ptr<ManifoldSurfaceMesh> mesh;
std::unique_ptr<VertexPositionGeometry> geometry;
std::tie(mesh, geometry) = readManifoldSurfaceMesh(filename);
// construct a solver
PoissonDiskSampler poissonSampler(*mesh, *geometry);
std::vector<SurfacePoint> samples = poissonSampler.sample(); // sample using default parameters
// Sample with some different parameters.
PoissonDiskOptions sampleOptions;
sampleOptions.minDist = 2.;
std::vector<SurfacePoint> newSamples = poissonSampler.sample(sampleOptions);
Helper Types
Options
Options are passed in to options via a PoissonDiskOptions object.
| Field | Default value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
double minDist |
1 |
The minimum distance r between samples, expressed in world-space units. |
int kCandidates |
30 |
The number of candidate points chosen from the (r,2r)-annulus around each sample. |
std::vector<SurfacePoint> pointsToAvoid |
std::vector<SurfacePoint>() |
Points which samples should avoid. |
double minDistAvoidance |
1 |
The radius of avoidance around each point to avoid, expressed in world-space units. |
bool use3DAvoidance |
true |
If true, the radius of avoidance will specify a solid ball in 3D space around which samples are avoided. Otherwise, samples are avoided within a geodesic ball on the surface. |
Using the use3DAvoidance option, the radius of avoidance minDistAvoidance can specify either the radius in 3D space, or in terms of distance along the surface. The former will produce a radius of avoidance that will appear perfectly round, and is likely more visually pleasing, but for very large radii may occlude samples from opposite sides of the mesh. The latter will restrict the radius of avoidance to only be along the surface, but such a metric ball may not appear perfectly round, especially in areas with very large changes in curvature.