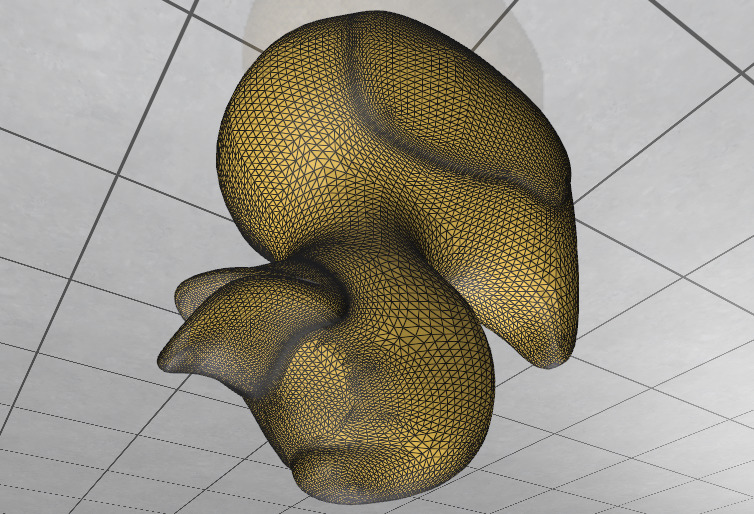
Basic Mutation
This tutorial explores the surface mesh data structure in geometry-central, via a simple example which splits and flips edges to perform 4:1 subidivision of a triangle mesh.
View full, runnable source code in the tutorial repository.
Basic setup
To begin we include headers, bring in namespaces, See the first tutorial for more info on these steps.
#include "geometrycentral/surface/manifold_surface_mesh.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/meshio.h"
#include "geometrycentral/surface/surface_mesh.h"
#include "polyscope/polyscope.h"
#include "polyscope/surface_mesh.h"
using namespace geometrycentral;
using namespace geometrycentral::surface;
Again as before, load an input mesh from file, and visualize it using Polyscope. Here, we’ll require that the mesh be manifold.
std::unique_ptr<ManifoldSurfaceMesh> mesh;
std::unique_ptr<VertexPositionGeometry> geometry;
std::tie(mesh, geometry) = readManifoldSurfaceMesh(args::get(inputFilename));
polyscope::init();
polyscope::registerSurfaceMesh("input mesh", geometry->vertexPositions,
mesh->getFaceVertexList());
// call polyscope::show(); to inspect the mesh at this point
Now, we’ll evaluate a 4:1 sudivision via the following algorithm:
- split each edge and connect to opposite vertices
- flip any new edge connecting a new to old vertex
First, we’ll create two MeshData<> containers. They associate data with mesh elements. We initialize them both with true values, because initially all vertices (resp. edges) are original. We’ll also track a list of edges to flip in the second phase.
VertexData<bool> isOrigVert(*mesh, true);
EdgeData<bool> isOrigEdge(*mesh, true);
std::vector<Edge> toFlip;
Now our main algorithm loop (commented inline).
for (Edge e : mesh->edges()) { // loop over all edges
if (!isOrigEdge[e]) continue; // don't keep processing new edges
// gather both vertices incident on the edge, and their positions
Vertex oldA = e.halfedge().tipVertex();
Vertex oldB = e.halfedge().tailVertex();
Vector3 oldAPos = geometry->vertexPositions[oldA];
Vector3 oldBPos = geometry->vertexPositions[oldB];
// split the edge
Vertex newV = mesh->splitEdgeTriangular(e).vertex();
isOrigVert[newV] = false;
// position the new vertex
Vector3 newPos = 0.5 * (oldAPos + oldBPos);
geometry->vertexPositions[newV] = newPos;
// iterate through the edges incident on the new vertex
for (Edge e : newV.adjacentEdges()) {
isOrigEdge[e] = false; // mark the new edges
Vertex otherV = e.otherVertex(newV); // other side of edge
// if this is a new edge between an old an new vertex, save for flipping
if (isOrigVert[otherV] && otherV != oldA && otherV != oldB) {
toFlip.push_back(e);
}
}
}
and finally, we can actually flip the edges to complete the second phase
for (Edge e : toFlip) {
mesh->flip(e);
}
we now register this new mesh with geometry-central
auto* psMesh =
polyscope::registerSurfaceMesh("subdiv mesh",
geometry->vertexPositions,
mesh->getFaceVertexList());
polyscope::show();
and as expected get the subdivided mesh.
Before:
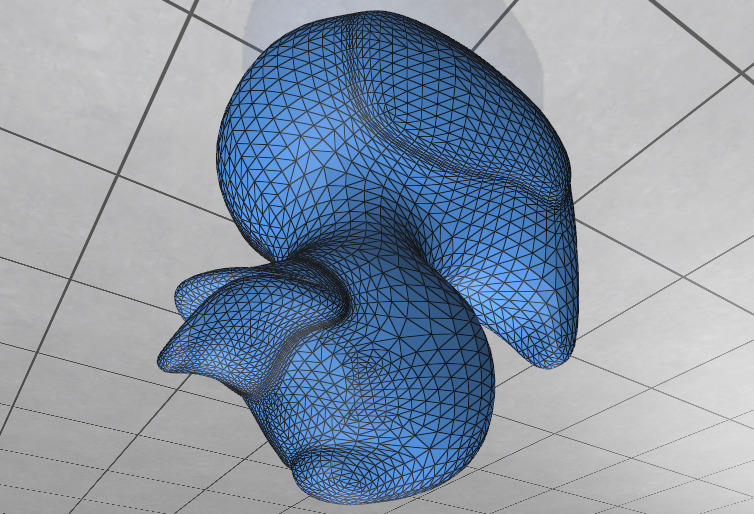
After: